Introduction
This article narrates the origin of Newar and Tharu who are two of the natives of Nepal; some Indian nationalists might find it too controversial to read.Homeland
The homeland of the Newar and Tharu is in the regions of Greater Lumbini and Kathmandu Valley of Nepal.The Newar got their name from Nepa which was historically the local name for Kathmandu/Nepa Valley.
They were originally Sino-Tibetan people related to the Kirat people in eastern Nepal. Sometime before 560 BC, the Tharu people migrated to Greater Lumbini in southern Nepal.
Buddha's kingdom
Siddhartha Gautama Buddha was born in Lumbini in 563 BC and he was a prince of Kapilvastu kingdom. This kingdom was situated next to Kiratdesh kingdom which has Trisuli River as its western border. These two kingdoms were contemporaries of each other.Queen Mayadevi, Gautama Buddha's mother, was born in Koliya kingdom which is in present-day Devadaha/Devdaha of Nepal.
 |
| Location of the earliest kingdoms in Nepal |
King Vidudabha of Kosala kingdom, from present-day Ayodhya of Uttar Pradesh (Northern India), destroyed Kapilvastu kingdom during Buddha's time; the people of Kosala kingdom are of Indo-Aryan ethnicity.
The ruins of Tilaurakot are the remains of ancient Kapilvastu kingdom.
Descendants of Kapilvastu
There are claims by several articles that Gautama Buddha's tribe, which was called Sakya clan in ancient times, are the ancestors of both ethnic Tharu and Newar.Both of these tribes are the descendants of ancient Kapilvastu and Koliya kingdoms. The present homeland of the Tharu is where Kapilvastu and Koliya kingdoms were situated which are Lumbini and Devadaha in Nepal.
Both of these claims are supported by evidences referred in the two links below.
https://kknews.cc/culture/y6v6ab.html (written in Chinese language)
The Sakya clan was claimed by Indian nationalists to be the Scythian people, an Iranic people who thrived in the grasslands of Central Asia but there is no linguistic evidence for this because there isn't any ethnic group in Nepal who speak Iranic languages nor is there any historical text supporting this.
The word Sakya was actually derived from the Sakhuwa tree which was their national tree in Kapilvastu.
When the king of Kosala kingdom attacked Kapilvastu out of revengeful thoughts for the Sakya people, many Sakya people were massacred and the remaining survivors lived in the southernly hills as the ancestors of Tharu and Newar people.
Culture of Newar-Tharu
Both the Newar and Tharu celebrate Maghe Sankranti festival which they celebrate by eating molasses and ghee after bathing in holy rivers and donating for charity.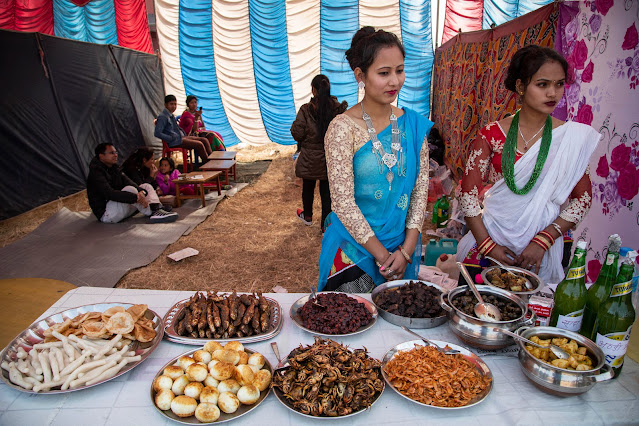 |
| Maghe Sankranti festival |
Another common attribute is eating snails. These common cultural aspects are further evidence that the two tribes were closely related in ancient times.
Buddha's ethnicity
It was always assumed by Indians that Buddha was Indo-Aryan because he spread Buddhism to India but many people do not realize that the natives of Nepal and the Himalayans/Tibetan plateau are the Sino-Tibetan people and not the Indo-Aryan people.
The Buddhist sutras were written in Sanskrit around 500 years after Buddha's death so his Indian disciples could have Sanskritized the original names. This is similar to how the Chinese gave Chinese names to some Buddhist gods like Kuan-Yin whose Sanskrit name is Avalokitesvara.
There might also be some Indo-Aryan cultural and linguistic influence on greater Lumbini/Terai region after Kosala's invasion.
The Indo-Aryan and Iranic people came from the Bactria-Margiana complex in present-day Afghanistan-Turkmenistan and practise culture such as caste and horse sacrifice. Buddha's clan did not practise this animal sacrifice culture and even opposed the caste system so Buddha's clan was not Indo-Aryan as claimed by some Indian nationalists.
The location of Lumbini at the foothills of Himalayan mountains, which is very near Kiratdesh, also pointed out that they were originally Sino-Tibetan people as the original homeland of all Sino-Tibetan people were in eastern Tibetan-Qinghai plateau high up in the mountains.
Whereas the earliest Indo-Aryan civilization in India were along the fertile Indus Valley in western India and much later, the low fertile plains of northern India.
There were 16 Indo-Aryan kingdoms recorded at the time of Buddha but these didn't include the two Buddha-related kingdoms i.e. Kapilvastu and Koliya. Note that Kosala kingdom didn't include the Buddha-related kingdoms before the invasion by Kosala kingdom.
Lumbini is also situated at a higher elevation hills than the Kosala kingdom with its capital at Shravasti (lower elevation) which is consistent with this fact.
During Buddha's time more than 2500 years ago, northern India had plenty of empty land and the Indo-Aryan people would prefer to live in the low plains where the weather is warmer.
Migration of Indo-Aryan people to Nepal
The Malla dynasty, ruled by the Indo-Aryan Bihari Maithili people who originated from northern India, invaded parts of present-day Nepal around the 13th century AD and later migrated mainly to the Greater Lumbini (Terai region) in southern Nepal.
The ethnic Newar can still speak their own Sino-Tibetan language; however, a few hundred years ago, the ethnic Tharu lost their original Sino-Tibetan language and adopted an Indo-Aryan language after the mass migration of Indo-Aryan people to southern Nepal who intermarried with the native Tharu (the genetic proof is given in one of the sections below).
The original language of the Tharu should be similar to Newar language as both descended from the same ancestor.
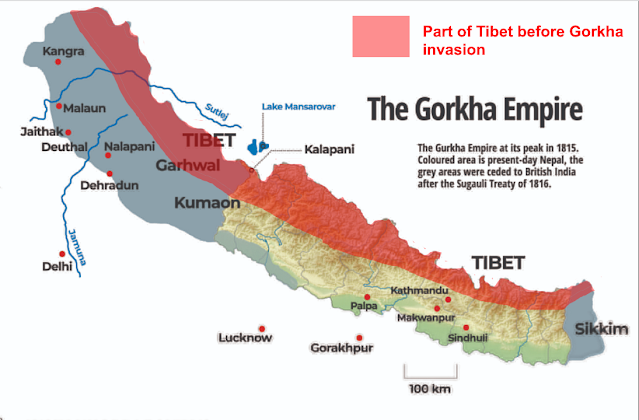
In 1769 AD, all the lands of the Maha-Kirat & Tharu-Newar people in central and southern part of present-day Nepal were invaded by the Gorkha Kingdom; which was ruled by the Indo-Aryan Pahari Khas people.
This triggered a massive migration of the Pahari Khas people to central Nepal to become the largest ethnic group in Nepal today. The Pahari Khas people is subdivided into several subgroups such as Chhetri and Khas Brahmin.
The Gorkha kingdom further invaded Tibet from 1788 to 1792 AD and incorporated parts of Tibet into present-day northern Nepal.
In fact, the Sino-Tibetan Newar language was still called the 'language of Nepal' and not the Indo-Aryan Khas language in 1380 AD. This goes to show that the Indo-Aryan people were not predominant in Kathmandu Valley until the 18th century AD.
The evidence from manuscripts and historical documents showed that the Newar language was originally known as 'Newa Bhaye' or 'Nepal Bhasha' from Nepal Samvat 500 (1380 AD) and came to be referred as 'Newar' by foreign scholars only from N.S. 880 (1760 AD) onwards; when 'Khasa Bhasa' (the Indo-Aryan Khas language) replaced Newar language as Nepal Bhasha (the language of Nepal).
Newar-Tharu subgroups
The subgroups of the Newar-Tharu people are as follows:- Newar (They call themselves Nepami or Newami which means the people of Nepa)
- Baram-Thami
- Tharu
- Chakma?
All these subgroups descended from the same people in Kapilvastu and Koliya thousands of years ago in Nepal.
 |
| Tharu people |
The adopted language of the Tharu people is actually from the Bihari language of the Malla dynasty and not from the Pahari Khas language of the Gorkha kingdom.
The Newar people most probably escaped to the higher hills when the Malla dynasty took over Greater Lumbini in southern Nepal; that is why their distribution is so scattered in small areas (red dot regions in the map below).
 |
| Thami people |
Origin of Chakma
The Chakma people are Buddhists who live in both Arakan of Myanmar and Chittagoing hills of Bangladesh. They call themselves Saksa which means 'descendants of Sak'. Chakma/Sakma is a Bengali corruption of the word Saksa. Sak should be the abbreviation of the original word Sakya.
The Chakma people claim to be descended from Buddha's Sakya clan. However, they lost their original language and speak an Indo-Aryan Bengali language so it is not possible to verify based on linguistic evidence.
They are certainly of East Asian race (not Indo-Aryan) and almost all scholars stated they are Sino-Tibetan people.
Their legends and songs stated that their original homeland is in Champak Nagar which some scholars stated to be probably in western Bihar state. Bihar state is very near Kapilvastu which provides evidence that they are probably from Buddha's clan.
 |
| Chakma girls |
In the long migration southwards, they were recorded to migrate to Northern Arakan in Myanmar and extended their territory to Chittagong Hill tracts of Bangladesh. The Arakanese (subgroup of the Burmic people) history text 'Dengawadi Aredfung' recorded the Chakma in 1118 AD so Chakma were already in Arakan by that year.
Interracial marriage
A certain percentage of both Newar and Tharu people married the Indo-Aryan people.
Here is the Tharu genetic chart that states they are genetically related to Tibetans with some Indo-Aryan genes. In other words, a certain percentage are of mixed race.
On average, Tharu people have around 60% O3a5/M134 (Sino-Tibetan haplogroup) and 40% R1a1/M198 (Indo-Aryan haplogroup).
Closest ethnic relatives
The closest ethnic relatives of the Newar and Tharu are the Maha-Kirat people such as Limbu, Rai, Magar and Chepang. Due to the location of the Maha-Kirat people on the higher Himalayan mountains, they were less mixed genetically than the Newar-Tharu whose homeland was in the lower Himalayan foothills where the Indo-Aryan people can reach with less effort.
Conclusion
The Newar and Tharu are the natives of southern Nepal and descended from the same Sino-Tibetan clan which is Sakya-Koliya thousands of years ago.
 |
| Newar people |
The invasion and migration of the Indo-Aryan people who came from northern India muddled/confused their true origin which is of Sino-Tibetan origin.
Related links
Ethnic origin of Mahakirathttp://eastasiaorigin.blogspot.com/2017/09/ethnic-origin-of-nepalese.html
Origin of Sino-Tibetan tribes
http://eastasiaorigin.blogspot.com/2018/08/origin-of-sino-tibetan-tribes.html
Sources
- The Newar Language: A Profile. By Tej R. Kansakar. Tribhuvan University, Kathmandu, Nepal. http://himalaya.socanth.cam.ac.uk/collections/journals/jns/pdf/JNS_01.pdf
- Benedict, Paul K. (1972) Sino-Tibetan: A Conspectus. Cambrid~e: Cambridge University Press
- https://kknews.cc/culture/y6v6ab.html
- Chakmas: Indigenous Peoples of Mizoram. By Paritosh Chakma.
- Genesis of Indigenous Chakma Buddhists and Their Pulverization Worldwide. By S. P. Talukdar.
- Source of genetic chart:
Copyright © eastasiaorigin.blogspot 2017-2022. All rights reserved.







Comments
Post a Comment